What are stem cells? These remarkable undifferentiated cells hold the potential to revolutionize healthcare by paving the way for personalized medicine tailored to individual needs. In this blog, we will explore the science behind stem cells and their transformative impact on regenerative medicine.
Reboot Your Health With Stem Cell Technology
Reboot Your Health with Stem Cell Technology – Try LifeWave X39! Commit to a 3-month trial and watch your energy, wellbeing, and vitality transform. Here’s the deal: – Wholesale Trial Price – Just $99/month for 3 months (total $297), with a one-time $20 fee for wholesale access. – Keep in mind there’s a small additional cost for shipping. – Retail Option – Prefer retail? The cost is $150/month for 3 months (total $450). We’re so confident in the results, if you’re not amazed after 3 months of following protocol, we offer a refund! Ready to reboot your health? Email us BELOW with the subject line “TechTest”to get started today. Take the step towards wellness with LifeWave X39 — you won’t look back!
🌱 What are stem cells?
Stem cells are unique cells in the body that possess the remarkable ability to develop into various types of cells. They are undifferentiated, meaning they lack a specific function until they receive signals to mature into specialized cells like muscle, nerve, or blood cells.
These versatile cells play a crucial role in growth, development, and healing. For instance, when your body needs to replace damaged or dead cells, stem cells provide a source for regeneration.

Understanding stem cells is essential for advancing medical treatments. They hold promise for therapies that can repair or replace damaged tissues and organs, making them a focal point in regenerative medicine.
🔬 Regenerative medicine
Regenerative medicine is a groundbreaking field that focuses on repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs. It leverages the unique properties of stem cells to restore health and functionality.
Stem cells are at the heart of this discipline. By harnessing their potential, scientists aim to develop innovative treatments for conditions that currently have limited options.
For example, in cases of heart disease, researchers are exploring ways to use stem cells to regenerate heart tissue, potentially reversing damage caused by a heart attack.
- Spinal cord injuries: Stem cells could help regenerate nerve cells, restoring movement and sensation.
- Diabetes: Research is underway to use stem cells to replace insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Osteoarthritis: Stem cells may help repair damaged cartilage in joints, reducing pain and improving mobility.
🧬 The Importance of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine tailors treatment plans to an individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment. This approach is particularly relevant in the context of stem cells.

By using a patient’s own stem cells, doctors can minimize the risk of rejection and improve the effectiveness of treatments. This is especially crucial for procedures like stem cell transplants.
Imagine a world where organs are grown from your own cells, eliminating the need for donors and reducing the risk of complications. This vision is becoming more feasible as research progresses.
- Enhanced treatment efficacy: Personalized therapies can lead to better outcomes.
- Reduced side effects: Using a patient’s own cells minimizes adverse reactions.
- Broader applications: Stem cells can be tailored for various conditions, from genetic disorders to chronic illnesses.
🧪 The Mechanism of Stem Cells
Understanding how stem cells function is key to unlocking their potential in medicine. They can divide and differentiate into specialized cells, a process influenced by internal and external factors.

Stem cells respond to signals from their environment, which guide them on how to develop. This mechanism is vital for tissue repair and regeneration.
Researchers are studying these processes to replicate them in laboratory settings, which could lead to breakthroughs in creating tissues for transplantation.
- Cell division: Stem cells can replicate themselves indefinitely.
- Differentiation: They can become specialized cells based on the body’s needs.
- Environmental signals: Factors like hormones and growth factors influence their development.
🩺 Stem Cells in Tissue Replacement
One of the most promising applications of stem cells is in tissue replacement. This involves creating new tissues to replace those damaged by disease or injury.
For instance, scientists are developing methods to grow skin tissues for burn victims, helping to heal wounds more effectively. Similarly, research is ongoing to create heart tissues to treat cardiovascular diseases.
These advancements could revolutionize how we approach organ transplants, significantly reducing the waiting list for donor organs.
- Skin regeneration: Stem cells are being used to create skin grafts for burn victims.
- Heart tissue engineering: Efforts are underway to develop heart tissues that can be implanted in patients.
- Bone and cartilage repair: Stem cells show promise in regenerating these critical tissues.
🩸 Stem Cells and Blood Diseases
Stem cells play a vital role in treating blood diseases, particularly leukemia. This form of cancer disrupts the production of healthy blood cells in the bone marrow.

In leukemia, abnormal cells proliferate, obstructing the growth of healthy stem cells. A stem cell transplant can introduce new, healthy stem cells to regenerate the blood cell population.
This method not only restores blood cell production but also enhances the patient’s immune system, vital for fighting off infections.
- Bone marrow transplants: The most common method for treating leukemia with stem cells.
- Peripheral blood stem cell transplants: Utilizing stem cells from the bloodstream.
- Umbilical cord blood transplants: Using stem cells stored from newborns’ umbilical cords.
Each of these approaches has its unique benefits and challenges, making ongoing research essential to refine these therapies.
🔍 Types of Stem Cells
Understanding the different types of stem cells is crucial for their application in medicine. Each type has unique properties and potential uses.
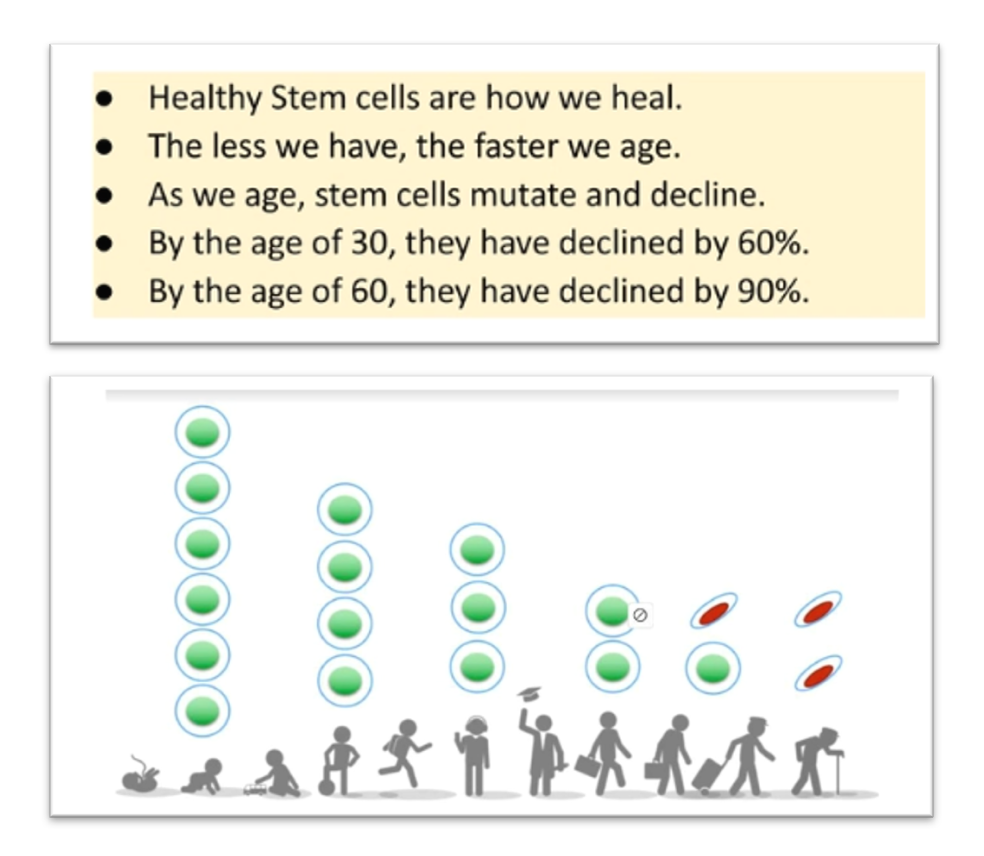
- Adult stem cells: Found in specific tissues, these cells are responsible for repairing and maintaining those tissues.
- Embryonic stem cells: Derived from embryos, they are pluripotent and can develop into any cell type.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): These are reprogrammed cells that mimic embryonic stem cells, offering vast research potential.
Each type of stem cell presents unique advantages, driving innovations in personalized medicine and regenerative therapies.
🧪 Research and Development in Stem Cell Therapy
Research in stem cell therapy is advancing rapidly. Scientists are exploring new techniques to enhance the efficacy of stem cell treatments.

Current studies focus on improving the methods of harvesting and transplanting stem cells, as well as enhancing their ability to differentiate into specific cell types.
Additionally, researchers are investigating the potential of gene editing technologies, like CRISPR, to correct genetic disorders at the stem cell level. This could lead to groundbreaking treatments for inherited diseases.
- Clinical trials: Ongoing trials are essential to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new stem cell therapies.
- Collaboration: Partnerships between academic institutions and biotech companies are fostering innovation.
- Ethical considerations: Addressing ethical concerns surrounding stem cell use is crucial for public trust and support.
🔮 Future Prospects of Stem Cell Research
The future of stem cell research holds tremendous promise. As technology advances, the potential applications of stem cells in medicine will likely expand.
Researchers are optimistic that stem cells could be used not only for treating diseases but also for developing organs for transplantation.
Imagine a world where organ transplants are no longer dependent on donor availability. This vision is within reach as scientists continue to explore the capabilities of stem cells.
- Regenerative therapies: Future treatments could allow for the regeneration of damaged organs and tissues.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatments to individual patients’ needs could become standard practice.
- Advancements in genetic engineering: This could lead to cures for genetic disorders by correcting mutations at the stem cell level.
❓ FAQS
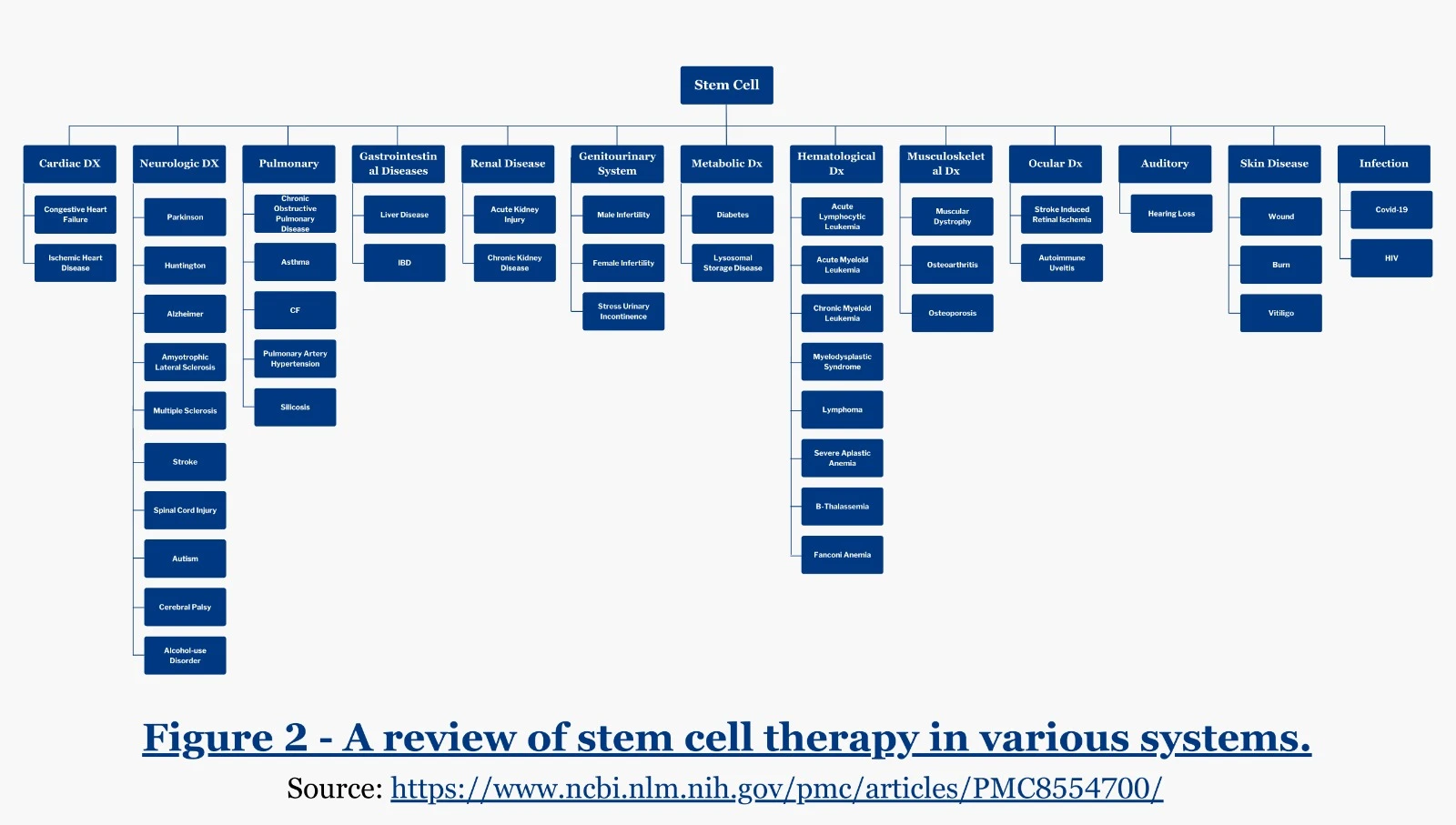
As interest in stem cells grows, so do questions surrounding their use. Here are some frequently asked questions – Expand and See all the systems where stem cells can play a role::
- What are stem cells? Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of developing into various specialized cell types.
- How are stem cells obtained? They can be sourced from embryos, adult tissues, or reprogrammed from other cell types.
- What diseases can stem cell therapy treat? Stem cell therapy is being researched for a range of conditions, including blood disorders, neurological diseases, and injuries.



