Cartilage surgery is a medical field that deals with fixing or replacing damaged cartilage. This tissue is key for support and flexibility in our bodies. It’s used in knee surgeries and in making noses look better through rhinoplasty.
Cartilage is vital for our joints. It helps us move smoothly and acts as a shock absorber between bones. Without it, we can face chronic pain and lose function, leading many to seek cartilage surgery and transplants.
In rhinoplasty, cartilage grafts are used to change the look or function of the nose. It can come from the septum, ear, or even from cadaver ribs. This method improves looks and can fix breathing issues and past surgery damage1.
For the best results, advanced tools like MRI are used to check how the graft is doing after surgery. This is done for up to a year2. Cartilage transplants have high success rates and few side effects, offering hope for those with cartilage damage2.
Key Takeaways
- Cartilage surgery includes fixing or replacing damaged cartilage in different body parts.
- For rhinoplasty, cartilage is often taken from the septum, ear, or rib, with cadaver ribs used for extra support1.
- Joint preservation surgery is key for those with knee cartilage damage, preventing long-term pain and mobility loss.
- Advanced imaging like MRI is crucial for monitoring cartilage transplant success up to a year after surgery2.
- Cartilage surgery and transplants can greatly improve joint and nasal function, as well as overall appearance.
Understanding Cartilage Surgery
Cartilage surgery is a modern medical procedure that fixes damaged cartilage in the body3. It helps people with joint problems or deformities3. Let’s explore what cartilage surgery is, the different types, and why it’s important.
What is Cartilage Surgery?
Cartilage surgery fixes or replaces damaged cartilage. It’s key for fixing joints and body parts like ears and noses. This surgery can greatly improve life quality, especially for young, active people34.
Types of Cartilage Surgery
There are many cartilage surgery procedures. Each one focuses on different aspects of fixing cartilage:
- Microfracture Surgery: It creates tiny bone fractures to grow new cartilage3.
- Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI): This uses the patient’s cells to fix cartilage defects4.
- Osteochondral Autograft Transfer System (OATS): It transplants healthy cartilage and bone to fix joint damage3.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Research is looking into their use for growing new cartilage, offering future hopes3.
The Importance of Cartilage in the Body
Cartilage is crucial for smooth joint movement and structure in parts like ears, noses, and knees. Repairing articular cartilage reduces pain and boosts mobility, making daily life better3. It’s also key for athletes and active people, helping them recover faster and get back to their activities4.
Understanding and treating cartilage damage through surgery is vital for joint health. It prevents further problems5.
DO This BEFORE SURGERY
Before you decide on knee cartilage repair surgery, it’s key to prepare well. You should know the risks and benefits of surgeries like meniscal allograft transplantation. Also, look into less invasive options like stem cell therapy. This could help with chronic pain and damage without surgery.
Meniscal allograft transplantation uses donor tissue and is for severe tears causing cartilage damage6. It comes with risks like nerve damage and stiffness6. But, it’s less risky than full knee replacement for those under 557.
Recovery is tough, needing a knee brace, crutches, and months of therapy6.
Getting ready for surgery is crucial. You might need to stop some meds and avoid food and drinks before7. Imaging tests like X-rays and MRI are also key to ensure the tissue is safe7.
| Aspect | Meniscal Allograft Transplantation | Meniscal Transplant Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Criteria | Severe meniscus tears with majority damage6 | Usually under age 55, missing >50% of meniscus7 |
| Main Risks | Nerve damage, stiffness, possible disease transmission6 | Stiffness, incomplete healing, minimal infection risk7 |
| Recovery | 6 weeks crutches, 4-6 months physical therapy6 | A few months, requires knee brace and crutches7 |
For chronic knee problems, try non-invasive treatments like stem cell therapy first. This might avoid the need for surgery, making recovery better.
Knee Cartilage Repair: Procedures and Benefits
Knee cartilage repair is key to easing pain and improving function. Techniques like autologous chondrocyte implantation and osteochondral grafting are very effective. These methods aim to boost knee mobility and slow down degenerative diseases.
Common Knee Cartilage Repair Techniques
Many methods are used for knee cartilage repair. Matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI) is best for cartilage damage over 2 centimeters8. Osteochondral autograft transfer is recommended for active people under 50 with small injuries8. Osteochondral fresh allograft transplant is for those under 50 with larger damage8.
Benefits of Knee Cartilage Repair
Knee cartilage surgery offers many benefits. It boosts joint stability and reduces pain, improving knee function. These surgeries target damaged areas, preserving the rest of the cartilage9. They also help prevent more severe conditions, allowing for a more active life8.
Recovery Process
The recovery from knee surgery involves rest, rehabilitation, and slowly getting back to activities. Minimally invasive surgeries like arthroscopy lead to less scarring and faster recovery9. After MACI, people can start jogging in 6 to 9 months8.
For osteochondral autograft transfer, returning to sports takes four to six months. Osteochondral fresh allograft transplant patients can start sports in about six months8.
Post-surgery care is crucial. Patients get medication to reduce swelling and pain, and they must avoid certain activities9. Regular check-ups with physical and occupational therapists help patients regain strength and function.
Orthopedic Surgery for Cartilage: Innovations and Advances
Orthopedic surgery for cartilage has seen big improvements. New techniques and technologies have changed the game. They help patients recover faster and get better results.
Improved grafting methods and advanced materials are key. These changes have made a big difference.
Latest Innovations in Orthopedic Cartilage Surgery
The CartiHeal™ Agili-C™ Cartilage Repair Implant is a new breakthrough. It’s shown great results in keeping knee cartilage healthy10. This FDA-approved implant uses aragonite, from coral, for advanced repair10.
Cassandra Lee, UC Davis Health’s sports medicine chief, says 40% of people over 40 and 25% of athletes will face cartilage issues10.
Stem Cell Technology in Cartilage Repair
Stem cell technology in orthopedics is changing cartilage repair. The Mayo Clinic’s RECLAIM procedure uses a patient’s cells and donor MSCs. It aims to grow new cartilage without donor DNA11.
This method could fill cartilage gaps in a year. It has the potential to help many joints11.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
New cartilage surgery offers many benefits. Alicia McHatton, a UC Davis Health nurse, saw big improvements with the CartiHeal implant. She could do physical therapy and regain strength in just six weeks10.
The RECLAIM procedure at Mayo Clinic can keep joints healthy for up to 20 years. It’s a long-term fix for cartilage problems11.
Patients with injury-induced problems can get better with surgery and stem cell tech. Those with chronic pain or diseases might find stem cell therapy more effective before surgery.
Cartilage Restoration Surgery: Options and Outcomes
Cartilage restoration surgery offers many cartilage repair options for joint problems from sports injuries or wear. The microfracture procedure creates small holes in the bone to grow new cartilage, good for small defects12. For bigger damage, the OATS procedure and osteochondral allografts are better. The OATS uses healthy cartilage from another knee area12, while allografts use donor cartilage for big damage12.
Matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI) is very successful. It takes healthy cartilage cells, grows them in a lab, and puts them back in the damaged area12. This method has a 74.3% success rate13 and helps a lot with joint recovery, but it takes longer to heal because of the two surgeries14.
The best method for each patient depends on their injury. Studies show autologous chondrocyte implantation works better (87.5%) than mosaicplasty (58%) for knee defects13. Microfracture is good for small damage, offering quick relief14. For big cartilage lesions, osteochondral allografts are best, with an 83% success rate after ten years13.
Recovery from cartilage surgery means using crutches, wearing a brace, and doing physical therapy12. Patients can usually go back to daily activities in four to six weeks. But, sports might take six months before you can start again14. These advanced options aim to ease pain, improve strength, and increase joint movement, helping you get back to normal activities and sports12.
| Procedure | Applications | Success Rate | Recovery Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microfracture | Small defects | 67% | 4-6 weeks12 |
| OATS | Smaller injuries | 82% | 6 months13 |
| Osteochondral Allograft | Significant areas | 83% | 6 months13 |
| MACI | Large defects | 74.3% | 12-18 months13 |
For more on regenerative therapy, check out stem cell technology and tissue engineering as cartilage repair options here.
Cartilage Grafting in Rhinoplasty
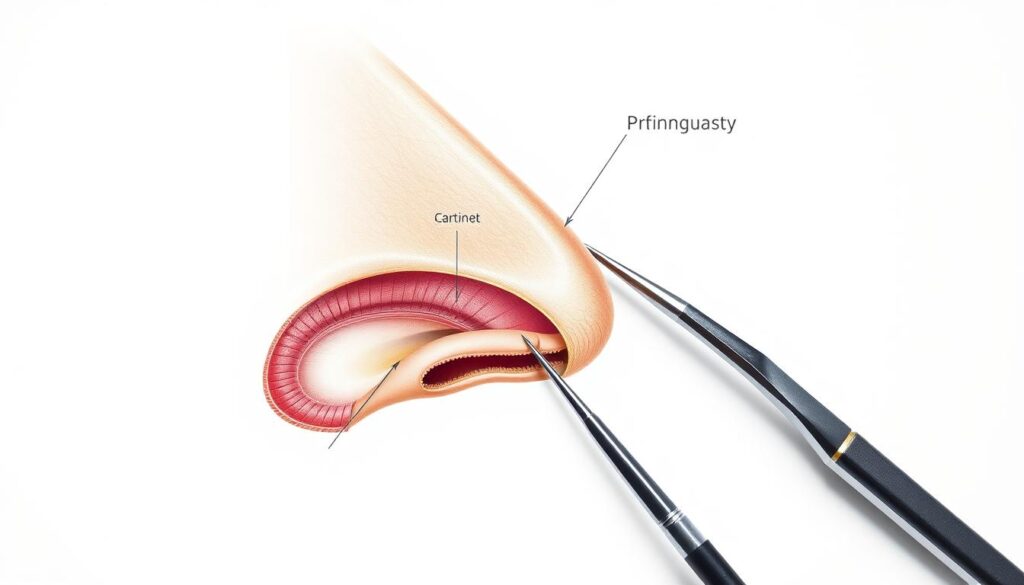
Cartilage grafting in rhinoplasty uses the patient’s own cartilage to fix nose issues. Surgeons often take cartilage from the ears, ribs, or nasal septum. This method helps improve the nose’s look and function15.
Using rib cartilage is good for complex nose reshaping. But, it might cause the cartilage to warp or lead to chest problems after surgery16.
Cartilage grafting can fix many nose problems like making the bridge higher or the tip more refined15. The septal cartilage is often chosen because it’s easy to shape and has fewer risks16. Yet, finding enough cartilage can be hard.
Conchal cartilage is great for second nose surgeries because it’s flexible and can be made thinner or thicker16.
For breathing issues or fixing past nose surgeries, doctors prefer cartilage from the septum, ears, or ribs. These grafts are good because they heal well and don’t cause much inflammation16. They help make the nose work better and look better, too16.
After the surgery, patients need to rest at home for 1 to 2 weeks. They should avoid hard activities like sports for 6 weeks to heal right15. Since nose surgeries can fail up to 21% of the time, choosing a skilled surgeon is key for success16.
| Types of Cartilage Grafts | Source | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Septal Cartilage Graft | Nasal Septum | Ease of sculpting, low infection risk | Donor site limitations |
| Ear Cartilage Graft | Auricular Concha | Versatility, variable thickness | Limited availability |
| Rib Cartilage Graft | Ribs (Costal) | Structural support for complex cases | Warping, post-operative chest issues |
Cartilage Surgery and Transplants
Cartilage surgery and transplants help fix damaged cartilage in the body. They are key for young, active people with injuries. These treatments can delay arthritis or avoid total knee replacement17.
We will look at autologous chondrocyte implantation, osteochondral grafting, and using allografts for big cartilage damage.
Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation
Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) uses a patient’s own cartilage cells. These cells are grown and then put back in the knee. It can improve the knee by up to 85% in a year18.
This method is best for people under 55 with big cartilage damage18. ACI often leads to great cartilage repair, making it a top choice for big damages18.
Osteochondral Grafting
Osteochondral grafting moves healthy cartilage to damaged areas. Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OAT) works for small damages18. Patients often recover quickly.
This method is good for small cartilage problems. It’s also a good option instead of cartilage transplant knee surgeries for small damages17.
Role of Allografts and Cadaver Cartilage
Allografts or cadaver cartilage are used for big cartilage defects. They come from donors and help with big damage. These transplants have about an 80% success rate17.
But, there can be problems like the cartilage growing too much or not fitting right17.
In summary, autologous chondrocyte implantation, osteochondral grafting, and allografts are key in modern orthopedic care. They give great results for the right patients. For those with chronic pain or big cartilage injuries, these treatments can change their lives.
Rhinoplasty with Rib Cartilage: How It Works
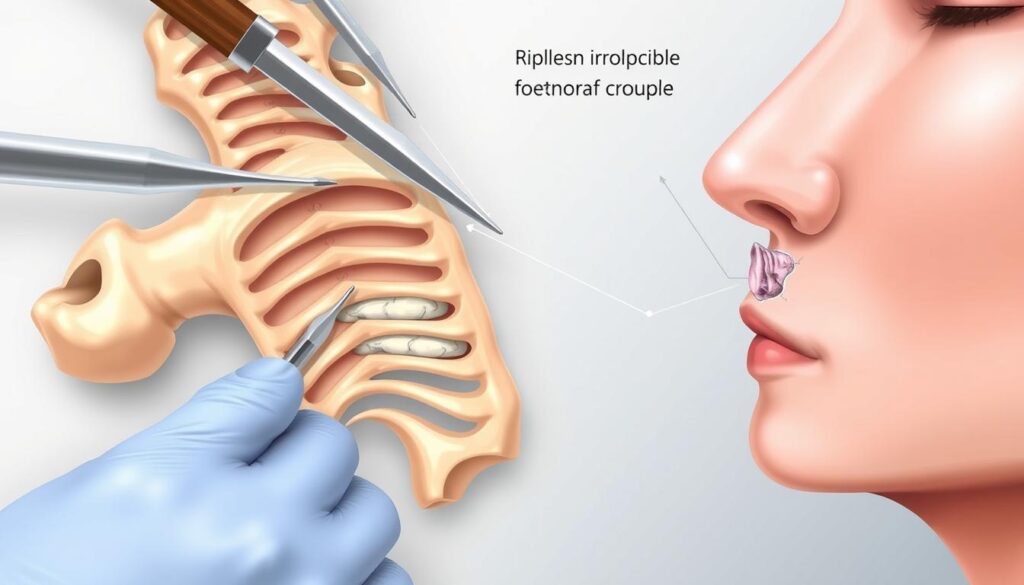
Rhinoplasty with rib cartilage is a special surgery. It uses cartilage from the rib to fix the nose. This method is great for those needing big changes to their nose.
Procedure Details
First, the surgeon takes cartilage from the rib. They make a small cut on the side of the chest, just below the breast. This cut is about 3-4 cm long, making scars less likely19.
Then, they shape the cartilage to fit the nose perfectly. This makes the nose look and work better.
The cartilage from the rib can be shaped in many ways. This makes sure the nose looks natural and unique for each person19. A skilled surgeon is needed to get the best results19.
For more details, you can read this article.
Benefits and Considerations
Using rib cartilage in rhinoplasty has many benefits. It’s strong, lasts long, and blends well with the body. This reduces infection risks and makes the nose look natural19.
But, there are things to think about. The chest scar might be visible, and recovery can be longer. You might feel pain and swelling in the chest for a while19.
Recovery can take a few weeks, and it may take six months to a year to see the full results. Despite this, the results last a long time. Rib cartilage rhinoplasty is often safer and more satisfying than using synthetic materials20.
Dr. Jacob Sedgh from Sedgh Facial Plastic Surgery is a top choice for this surgery. He’s known for his expertise in using rib cartilage grafts19.
Evolving Techniques in Cartilage Transplants for Knee
New methods in cartilage transplantation are making knee surgery better. These advancements lead to stronger and more functional results. This greatly improves recovery and success rates for patients.
New Techniques and Technologies
Recently, new approaches have been developed for cartilage transplantation. Matrix-assisted chondrocyte implantation (MACI) is a top choice. It offers faster recovery and long-lasting cartilage repair21.
Nanofracture tools are also gaining popularity. They outperform older methods like microfracture. These tools lower the chance of cysts and stiffness21. Autologous osteochondral grafting in knees is another key innovation. It focuses on the knee’s mechanics for better repairs22.
Patient Outcomes and Success Rates
Improved surgery techniques have greatly boosted patient results. For example, the Agili-C implant has shown great results. In a 24-month study, 75% of patients saw their cartilage defects filled with new tissue21.
MACI has been shown to last up to 15 years. It greatly reduces pain and boosts athletic performance21. Osteochondral allograft transplantation (OCA) also offers long-term healing for deep bone injuries21.
The future of cartilage transplantation looks promising. Thanks to new techniques, patients can expect better lives and recovery.
Conclusion
Cartilage surgery has made big strides, offering hope for those with joint and nasal cartilage problems. A 2015 review compared different knee surgeries, showing their effectiveness23. Another review in 2016 looked at a specific transplant method, showing its long-term benefits23.
New techniques and technologies are making cartilage repair more possible. For example, a method called autologous chondrocyte implantation has shown good results in studies24. Stem cell therapy is also gaining attention, especially for chronic pain and diseases.
Choosing the right surgery and using the latest methods are key to better results. This approach helps patients regain their activity levels and improve their quality of life. The ongoing research in cartilage surgery is crucial for better patient outcomes and recovery.
FAQ
What is Cartilage Surgery?
Cartilage surgery is a set of medical procedures. They aim to fix or replace damaged cartilage. This is key for keeping joints and body parts like the ear and nose working right.
What are the types of Cartilage Surgery?
There are many types, like knee cartilage repair and transplant procedures. Joint preservation surgery and rhinoplasty with cartilage grafting are also common. Techniques like autologous chondrocyte implantation and osteochondral grafting are used too.
What is the importance of cartilage in the body?
Cartilage lets joints move smoothly and keeps body parts like the ear, nose, and knee joints in shape. It supports structure and adds flexibility, which is crucial for moving well and looking good.
What should patients do before undergoing knee cartilage repair or other orthopedic procedures?
Before surgery, try non-invasive treatments like stem cell therapy to ease pain. This might help avoid surgery. Getting ready for surgery is very important for good results.
What are the common techniques used in knee cartilage repair?
Common methods include autologous chondrocyte implantation and osteochondral grafting. These aim to fix knee function, reduce pain, and boost mobility.
What are the benefits of knee cartilage repair?
Benefits include better mobility, less pain, and slowing down degenerative diseases. A successful surgery can greatly improve life quality.
What does the recovery process entail after knee cartilage repair?
Recovery means resting, following a rehab program, and slowly getting back to normal. Listening to the surgeon helps heal faster and better.
What are the latest innovations in orthopedic cartilage surgery?
New advancements include better grafting methods, stem cell technology, and less invasive surgeries. These bring quicker recovery, less pain, and better results.
How does stem cell technology assist in cartilage repair?
Stem cells might grow new cartilage and ease pain with less surgery. This method is being studied to get even better.
What are the advantages of these new methods over traditional cartilage surgery?
New methods offer faster healing, less surgery, and better results. They aim for lasting solutions to cartilage issues.
What are the options available for cartilage restoration surgery?
Options include autologous chondrocyte implantation, osteochondral grafting, and using allografts or cadaver cartilage. The right choice depends on the damage and what the patient wants.
How is cartilage grafting used in rhinoplasty?
In rhinoplasty, cartilage grafting uses the patient’s own cartilage. It’s taken from the septum, ear, or rib to fix or enhance the nose. This improves both function and looks.
What is autologous chondrocyte implantation?
This method takes the patient’s cartilage cells, grows them in a lab, and then implants them in the damaged area. It helps grow new cartilage and repair the area.
What is osteochondral grafting?
Osteochondral grafting moves healthy cartilage from a non-weight-bearing area to a damaged area in the knee. It aims to fix the joint surface and ease pain.
What role do allografts and cadaver cartilage play in cartilage repair?
Allografts and cadaver cartilage are used for big defects that can’t be fixed with the patient’s own cartilage. They offer a solution for major cartilage damage.
How does rhinoplasty with rib cartilage work?
Rhinoplasty with rib cartilage uses rib cartilage to rebuild the nose. It’s for big reconstruction needs and can give a tailored look, but it has scarring and longer recovery risks.
What are the benefits and considerations of using rib cartilage in rhinoplasty?
Using rib cartilage can give a custom look and better nose structure. But, it might cause scarring and take longer to recover than other methods.
What are the new techniques in cartilage transplants for the knee?
New techniques include better grafting and using advanced tech like 3D printing for cartilage scaffolds. These aim to improve success rates and patient outcomes.
What are the outcomes and success rates of these new cartilage transplant techniques for the knee?
Success rates and outcomes are getting better thanks to new surgery methods and better care. These advancements help in quicker recovery and keeping joints healthy for longer.
Source Links
- What Is a Cartilage Grafting Nose Job?
- Three-dimensional changes of noses after transplantation of implant-type tissue-engineered cartilage for secondary correction of cleft lip–nose patients
- Articular Cartilage Restoration – OrthoInfo – AAOS
- Cartilage Repair FAQs for Patients
- Cartilage Graft – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
- Meniscal allograft transplantation Information | Mount Sinai
- Meniscal Transplant Surgery
- Surgery for Knee Cartilage Injuries
- Cartilage Repair Surgery & Treatment | Aurora Health Care
- New implant helps repair knee cartilage in UC Davis Health patients
- Mayo Clinic offers unique regenerative medicine procedure for knee and hip joints hopes to expand to other injuries – Mayo Clinic
- Cartilage Restoration Surgery | MedStar Health
- Current Concepts of Articular Cartilage Restoration Techniques in the Knee
- Latest Advances in Cartilage Repair and Regeneration | HSS
- Cartilage Graft Nose Jobs: What You Need to Know
- Grafting in revision rhinoplasty
- Knee Cartilage Transplant Procedures Chillicothe OH – Knee Pain Treatment
- Cartilage Transplant
- Rib Cartilage Rhinoplasty Procedure | Los Angeles, CA
- Revision Nose Job Rib Cartilage | Dr. Anthony Bared
- New techniques emerge amid the evolution of cartilage repair
- Clinical Cartilage Restoration: Evolution and Overview
- Assessment of Outcomes After Multisurface Osteochondral Allograft Transplantations in the Knee
- Twenty-Two-Year Outcome of Cartilage Repair Surgery by Perichondrium Transplantation

![[Understanding the Role of Genetics in Nutrition]](https://stemcelltreatmentprogram.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/understanding-the-role-of-genetics-in-nutrition.png)
![[The Science Behind Nutrition: What You Should Know]](https://stemcelltreatmentprogram.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/the-science-behind-nutrition-what-you-should-know.png)
